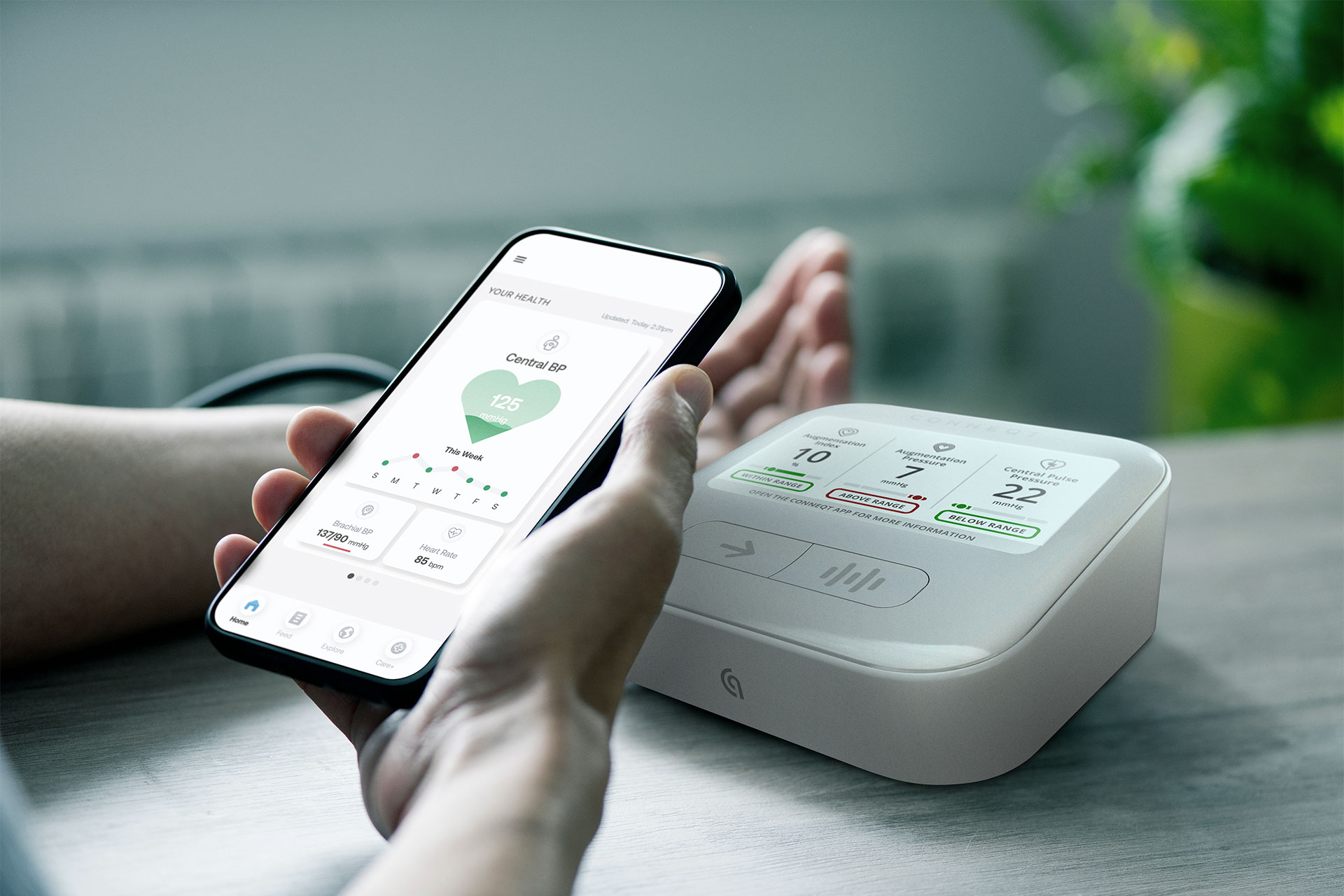
In a Heartbeat
- What is Central Blood Pressure (CBP)? Central blood pressure is the pressure in the aorta, the large artery that receives blood directly from the heart. It’s measured closest to the heart and major organs—offering a more accurate reflection of the force your cardiovascular system is experiencing with each beat.
- Why Does It Matter? CBP is often a more reliable predictor of cardiovascular events like heart attack, stroke, and kidney disease than traditional arm (brachial) pressure. It directly reflects arterial stiffness—a critical factor in vascular aging—and can differ significantly from brachial blood pressure by up to 40 mmHg. Understanding your CBP gives you insight into risks that standard blood pressure readings might miss.
- How is It Measured? The Pulse uses pulse wave analysis (PWA) powered by SphygmoCor® technology to measure CBP non-invasively. It captures and analyzes the waveforms created by each heartbeat to determine pressure at the aortic root, right where it matters most.
- Actionable Insights: Monitoring CBP over time helps track how your arteries and heart are adapting to age, lifestyle, and treatment. Elevated CBP may indicate increased arterial stiffness or heightened cardiovascular risk—even if brachial pressure appears normal. Lifestyle improvements like regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress reduction can help lower CBP and support healthier arteries.
- What This Means for You: By measuring CBP alongside brachial blood pressure, the Pulse gives you a fuller picture of your cardiovascular health. This dual insight allows for more personalized, early detection of cardiovascular risks and empowers you to take action before problems develop.
What is Central Blood Pressure?
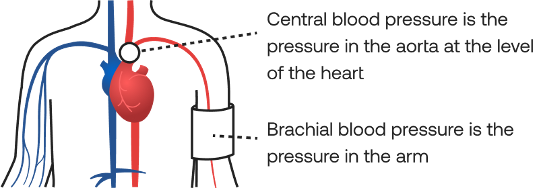
Central blood pressure (CBP) represents the maximum pressure faced by the heart and major organs and can differ by up to 40 mmHg from traditional systolic blood pressure measurements taken using a standard blood pressure device. It is a key measurement taken from the aorta, the main artery that receives blood directly from the heart and supplies it to the rest of the body.
Unlike brachial blood pressure measurements you might be familiar with from a doctor’s visit, CBP is the pressure right at the source—where it impacts your heart and major organs the most. This makes it a powerful tool for understanding vascular health.
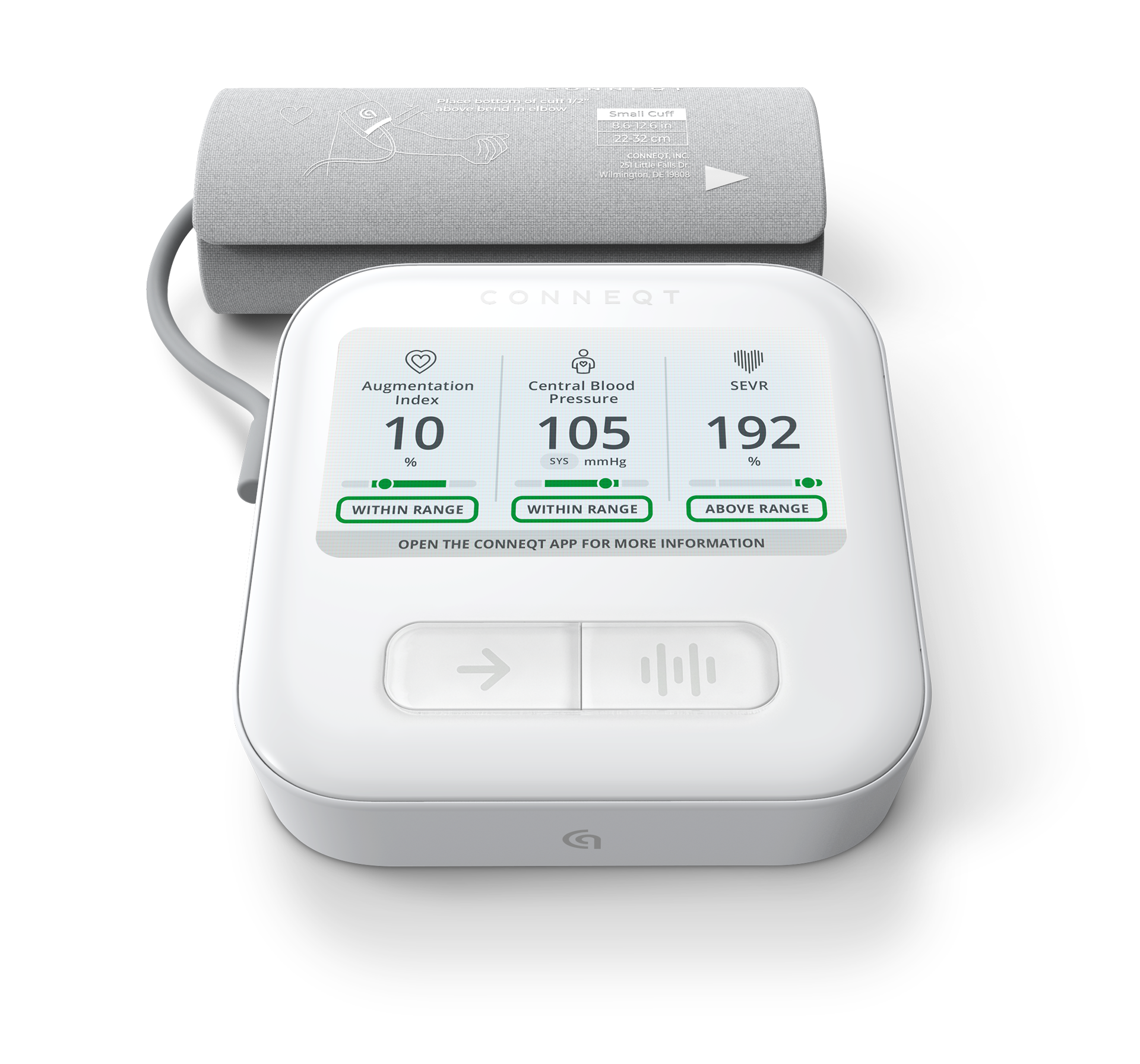

Medical Grade, Accurate, FDA-Cleared Heart Insights.
Save 20% on checkout with code VITALITY
This measurement provides a deeper insight into your cardiovascular health—especially when paired with brachial blood pressure. While brachial pressure is still important and widely used in clinical settings, central blood pressure reveals key cardiovascular risks that arm cuff measurements may miss.
Central blood pressure also doesn’t always move in lockstep with brachial readings. In some cases, brachial pressure may appear normal while central pressure is elevated—a condition called isolated central hypertension. Research shows this group carries some of the highest cardiovascular risk, underscoring why both numbers are essential to measure side by side.
Why is Central Blood Pressure Important?
To gain an accurate understanding of cardiovascular risk, it is crucial to measure central blood pressure as it directly reflects factors such as arterial stiffness—the rigidity of the blood vessels. As people age, their arteries, particularly the large aortic ones become less elastic and more stiff which increases CBP and the heart’s workload. CBP is a more reliable and sensitive predictor of cardiovascular conditions than traditional brachial blood pressure, more effectively predicting the risk of heart disease, stroke, vascular disease, and kidney failure. Understanding both your CBP and brachial pressure offers a comprehensive overview, enabling better health assessment and timely intervention that could prevent serious cardiovascular issues before they arise.
How is Central Blood Pressure Measured?
The CONNEQT Pulse utilizes advanced, non-invasive technology, including the integration of SphygmoCor® technology, to measure your CBP and other arterial biomarkers that traditional blood pressure devices do not provide. This process involves pulse wave analysis (PWA), which estimates the pressure in your aorta based on the waveforms generated by each heartbeat. These waveforms represent key functions of the heart with how it contracts (squeezes), how it relaxes, and how it generates pressure to provide blood flow to the body. This method not only captures the peaks (known as systolic) and troughs (known as diastolic) of your heart’s activity but also analyzes the shape and characteristics of the pulse wave, providing detailed information about the stiffness and health of your arteries.
What do My Results Mean?
Your central blood pressure (CBP) results are classified into personalized ranges tailored to your individual health profile. These ranges are based on data from a large clinical study that examined vascular health in over 4,000 people across a wide range of ages, sexes, and body types. This research created a detailed picture of how central blood pressure typically changes over time in a population without cardiovascular disease.
By comparing your CBP results to this healthy reference population, the Pulse helps determine whether your measurements fall within the expected range for someone like you—giving you a clearer view of your current cardiovascular health.
The ranges below explain what your CBP score may indicate about your cardiovascular risk.
Reference Ranges:
- Below Range: Indicates that your CBP is lower than the optimal range for your specific profile. This could be due to factors such as dehydration, medications, or certain cardiovascular conditions such as cardiomyopathy or valve diseases. While this might not be immediately concerning, it is important to monitor your readings and consult with your healthcare provider if you have any concerns.
- Within Range: This range is considered optimal for you and reflects a healthy cardiovascular state based on comparisons to 90% of the healthy population. Your results in this range are consistent with what is generally expected for someone of your age, sex, and height.
- Above Range: A CBP reading that falls above the optimal range may indicate an elevated risk of cardiovascular disease. This could prompt the need for further medical assessment and proactive intervention, as it may represent a value seen in only 5% of the healthy population and could be potentially less optimal for your profile.
Regularly tracking your CBP and understanding these ranges are crucial for maintaining or achieving optimal cardiovascular health. This tailored approach supports better decision-making regarding treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and ongoing health management.
How Do I Improve and Maintain My Central Blood Pressure?
Lowering central blood pressure (CBP) is one of the most effective ways to reduce the strain on your heart and major organs. Because CBP reflects the true pressure your body experiences at the root of the aorta, reducing it requires strategies that target arterial stiffness, improve vascular tone, and support overall cardiovascular function. Below are evidence-based actions you can take to improve your CBP and long-term heart health.
- Follow an Anti-Inflammatory Diet: A Mediterranean-style diet helps reduce arterial load and supports healthy vascular tone. Focus on vegetables, fruits, legumes, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and lean proteins. Prioritize foods that naturally enhance nitric oxide production—such as beets, arugula, spinach, and citrus—to improve arterial relaxation. Increase potassium intake through foods like bananas, avocado, and sweet potatoes to counterbalance sodium and reduce pressure in the aorta. Limiting ultra-processed foods, added sugars, and high-sodium meals is key to minimizing fluid retention and arterial constriction.
- Supplement Strategically: Targeted supplements may help lower CBP when used under medical guidance. Magnesium (200–400 mg/day) supports smooth muscle relaxation and vascular tone, while CoQ10 (100–200 mg/day) helps improve heart energy metabolism and reduce oxidative stress. L-citrulline and L-arginine promote nitric oxide synthesis, aiding in vessel dilation. Omega-3 fatty acids reduce inflammation and improve endothelial function. Potassium supplementation can also be beneficial if dietary intake is insufficient and blood levels are monitored.
- Start a Targeted Exercise Plan: Regular aerobic exercise strengthens the heart and reduces central pressure. Aim for 30–60 minutes of moderate activity (e.g., walking, swimming, cycling) most days of the week. Combine this with resistance training two to three times per week to improve vascular compliance. Adding one to two high-intensity interval training (HIIT) sessions weekly can further enhance nitric oxide availability and arterial elasticity, especially in those with elevated CBP.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Even modest weight loss can significantly lower central pressure by reducing the load your heart must pump against. Focus on sustainable lifestyle changes—such as mindful eating, reducing portion sizes, and increasing daily activity—that help support long-term cardiovascular resilience.
- Prioritize Stress Reduction: Chronic stress increases sympathetic nervous system activity and can elevate CBP. Techniques like meditation, yoga, deep breathing, and guided imagery help regulate blood pressure by reducing cortisol and improving parasympathetic tone. Monitoring heart rate variability (HRV) may provide insight into your body’s stress response and recovery patterns.
- Optimize Sleep: Sleep plays a vital role in cardiovascular regulation. Aim for 7–9 hours of high-quality sleep each night to support overnight blood pressure dipping, autonomic balance, and arterial repair. Inconsistent or insufficient sleep can increase morning CBP and impair recovery, even in healthy individuals.
- Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol: Tobacco significantly increases arterial stiffness and elevates both central and brachial pressure. Quitting smoking is one of the most powerful interventions to improve vascular health. Alcohol should be limited to no more than one drink per day for women and two for men, as even moderate use can increase central pressure by raising oxidative stress and disrupting normal vascular tone.
- Monitor Your Progress with the Pulse: Tracking your CBP regularly with the CONNEQT Pulse allows you to see how lifestyle changes, medications, and other interventions are affecting your cardiovascular health over time. This data can help guide adjustments and support more personalized care in partnership with your healthcare provider.
By implementing these strategies and tracking your progress with the Pulse, you can reduce excess pressure on your heart and arteries and improve your long-term cardiovascular health. For more daily guidance, build lasting habits with our free 28-day Arterial Wellness Program, developed with the American Heart Association and featuring daily tasks and expert tips.
Empowering Your Heart Health Journey
By regularly monitoring and understanding your CBP and other arterial biomarkers with the Pulse, the world’s most advanced personal arterial health monitor, you can take proactive steps towards maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system from the comfort of your home. This cutting-edge technology empowers you to make informed decisions about your health, potentially reducing your risk of serious cardiovascular conditions and enhancing your overall well-being.








