In a Heartbeat:
- What is Brachial Blood Pressure? Brachial blood pressure measures the pressure of blood against the walls of the brachial artery in your upper arm. It includes two key values: systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP).
- Why Does It Matter? Monitoring your brachial pressure is essential for detecting and managing hypertension, a leading risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure. It helps assess the strain on your cardiovascular system.
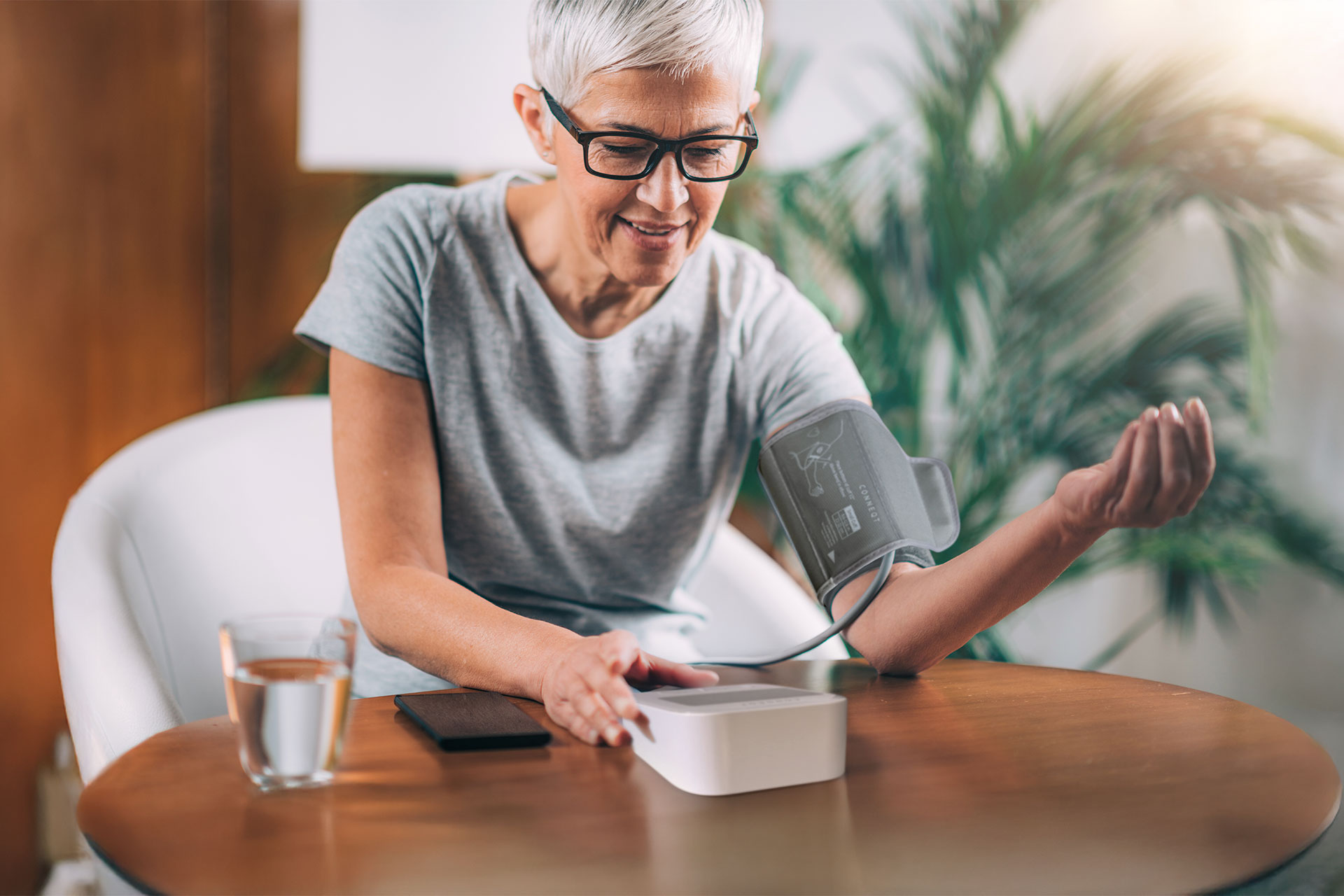
- How is it Measured? The CONNEQT Pulse uses advanced inflation-based technology to measure brachial pressure. It captures SBP and DBP along with additional cardiovascular parameters.
- Actionable Insights: Regularly tracking your brachial pressure empowers you to take control of your heart health. By identifying trends early, you can make lifestyle changes or seek treatment to maintain optimal cardiovascular health.
What is Brachial Blood Pressure?
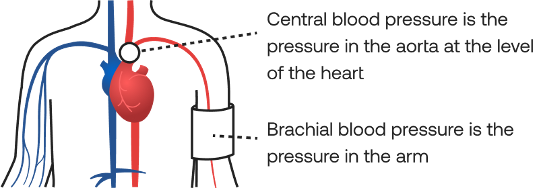
Brachial blood pressure refers to the pressure exerted by circulating blood on the walls of the brachial artery in the upper arm. This measurement is expressed using two key values. Systolic blood pressure (SBP) indicates the maximum pressure during the heart’s contraction. Diastolic blood pressure (DBP) reflects the minimum pressure when the heart relaxes between beats. Together, SBP and DBP provide important insights into your cardiovascular health by indicating the force your blood exerts on your arteries throughout the cardiac cycle. While brachial blood pressure focuses on the pressure within the arteries of your upper arm. This differs from Central Blood Pressure (CBP), which measures pressure closer to the heart and major organs. Both measurements are essential for a comprehensive understanding of your cardiovascular condition, each offering unique perspectives on your heart health.
Why is Brachial Blood Pressure Important?
Brachial blood pressure is an important indicator of your overall cardiovascular health. It directly measures the force exerted on your arteries during each heartbeat. Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a leading risk factor for severe cardiovascular conditions such as heart attacks, strokes, and kidney disease. Monitoring both SBP and DBP is crucial because elevated readings in either can signal an increased cardiovascular risk. While SBP and DBP alone often increase with age due to stiffening arteries, they both can increase because of common medical conditions that cause arterial stiffness, such as diabetes, high cholesterol, obesity, and kidney disease. An elevated DBP itself can also indicate health issues, particularly in younger individuals. Understanding and managing your brachial blood pressure is key to maintaining heart health and preventing the progression of hypertension, making it a critical tool in the ongoing assessment of your cardiovascular system.

Medical Grade, Accurate, FDA-Cleared Heart Insights.
Save 20% on checkout with code VITALITY
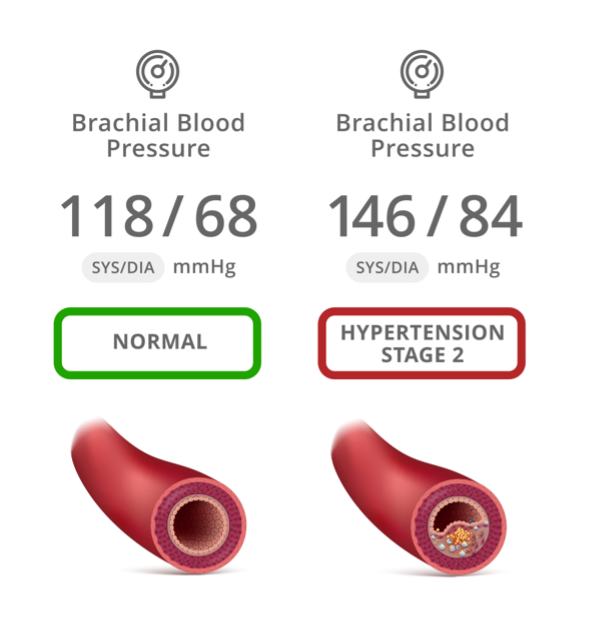
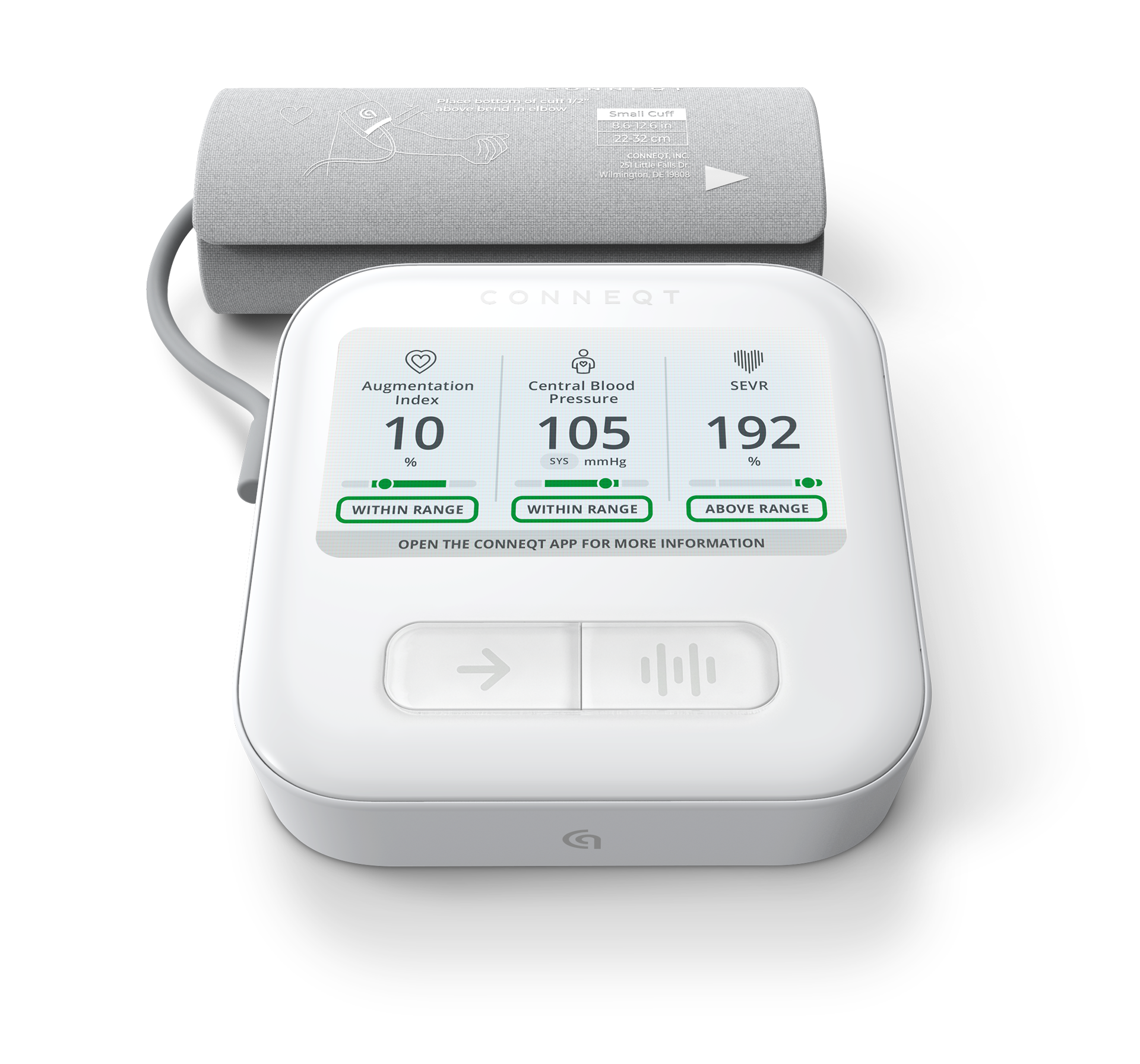
How is Brachial Blood Pressure Measured?
The CONNEQT Pulse utilizes advanced technology to measure brachial blood pressure (BBP) differently from traditional blood pressure monitors. Instead of capturing readings during the deflation process, the Pulse uniquely captures BBP during cuff inflation. This method provides accurate and reliable measurements of both systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP).
When using the Pulse, you may notice that the process differs from other devices. First, the cuff inflates to a level where BBP is captured. After this initial reading, the cuff inflates again to a pressure just below your systolic blood pressure. At this stage, the Pulse captures additional parameters, including central blood pressure (CBP), which provides deeper insights into your vascular health.
This dual-capture of BBP and CBP allows for a more comprehensive understanding of your cardiovascular system. This approach not only measures standard blood pressure values but also provides important insights into your heart’s workload and overall vascular function.
What Do My Results Mean?
Your brachial blood pressure results are classified into categories based on the American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines. These categories help you understand your cardiovascular health by comparing your readings to established thresholds that define normal blood pressure, elevated blood pressure, or hypertension.
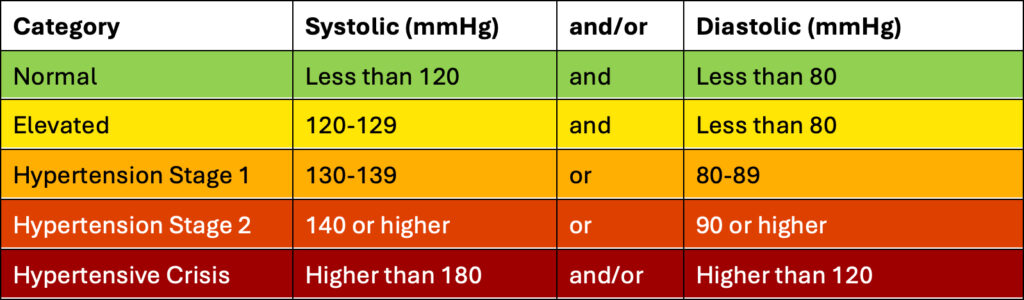
Reference Ranges:
- Normal: This range indicates that your blood pressure is within the optimal range for cardiovascular health. Maintaining readings in this range helps reduce the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other serious health issues. Normal blood pressure is defined as an SBP of less than 120 mmHg and a DBP of less than 80 mmHg.
- Elevated: Blood pressure in this range is higher than normal but not yet at the threshold for hypertension. Elevated blood pressure is defined as an SBP of 120-129 mmHg and a DBP of less than 80 mmHg. While not classified as hypertension, elevated blood pressure is a warning sign that you should make lifestyle changes and seek further evaluation by your healthcare professional to prevent the progression to hypertension.
- Hypertension Stage 1: This stage is the first stage of hypertension, where either your SBP or DBP falls within this range. Hypertension Stage 1 is defined as an SBP of 130-139 mmHg or a DBP of 80-89 mmHg. At this stage, there is an increased risk of cardiovascular disease such as heart attack and stroke over time. It may be necessary to discuss treatment options with your healthcare provider.
- Hypertension Stage 2: This stage indicates more severe hypertension, where either your SBP or DBP falls within this range. Hypertension Stage 2 is defined as an SBP of 140 mmHg or higher or a DBP of 90 mmHg or higher. This range represents a significant risk for cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attack and stroke. It typically requires more immediate medical attention and lifestyle changes.
- Hypertensive Crisis:
Contact your physician immediately.
Readings in this range should be repeated and if still elevated or if associated with any symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, headache, weakness, dizziness, rapid heartbeat, or any other symptoms you should immediately contact your physician or call 911 to seek emergency care.
Hypertensive crisis is defined as a SYS of 180 mmHg or higher and/or a DIA of 120 mmHg or higher.
Regularly tracking your blood pressure and understanding these ranges are essential for maintaining or achieving optimal cardiovascular health. This approach supports better decision-making regarding treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and ongoing health management.
How Do I Improve and Maintain My Brachial Blood Pressure?
Improving your brachial blood pressure is essential for maintaining heart health and preventing cardiovascular diseases. This requires a comprehensive approach involving several key lifestyle changes. Below are actionable strategies:
- Follow an Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Adopt a Mediterranean diet rich in vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds, whole grains, and lean proteins to support arterial health. Prioritize a variety of fruits and vegetables daily to increase potassium intake and boost vascular health—small changes, like adding an extra serving to each meal, can make a big difference. Include omega-3-rich foods like salmon and flaxseeds, and minimize processed foods, refined sugars, and trans fats. Foods like beets, spinach, and citrus fruits enhance nitric oxide levels, promoting arterial relaxation. A diverse diet also supports a healthy gut microbiome, which reduces inflammation.
- Supplement Strategically: Use magnesium (200–400 mg/day) to improve vascular tone and CoQ10 (100–200 mg/day) to reduce oxidative stress. L-arginine and L-citrulline enhance nitric oxide production, while Vitamin D and K2 prevent arterial calcification. Potassium-rich foods or supplements can further support blood pressure regulation.
- Start a Targeted Exercise Plan: Perform 30–60 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise 4–5 times per week, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling. Include resistance training 2–3 times weekly and add 1–2 high-intensity interval training (HIIT) sessions for maximum cardiovascular benefits.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight contributes to arterial stiffness. Focus on gradual, sustainable weight loss through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Prioritize Stress Reduction: Manage stress with mindfulness, yoga, or deep breathing to lower cortisol and improve vascular health. Consider heart rate variability (HRV) tracking to optimize stress responses.
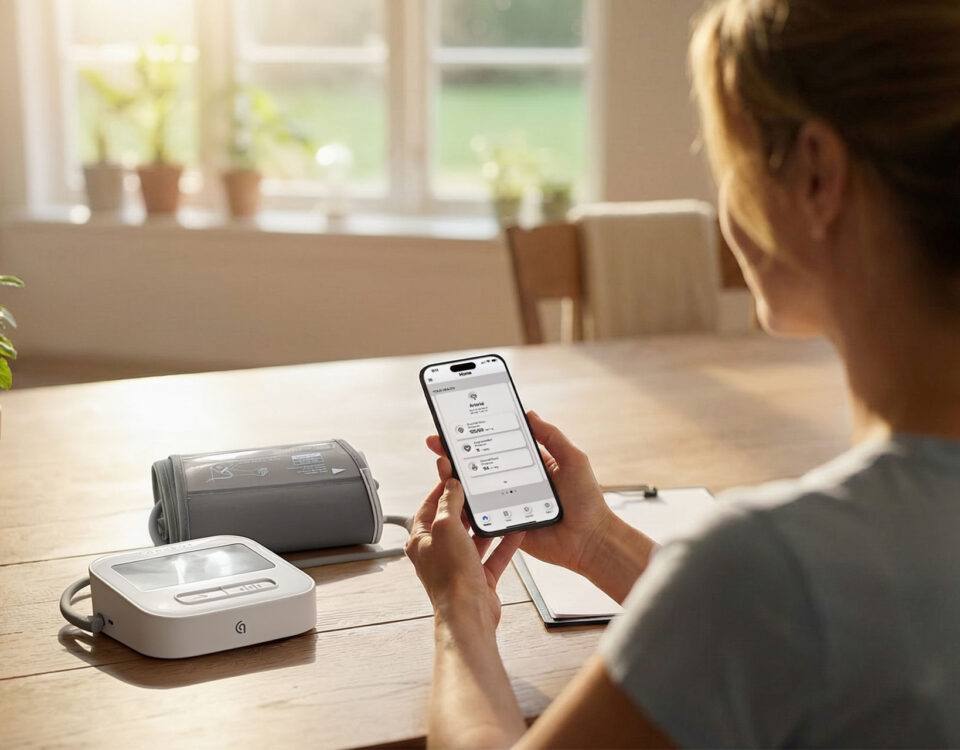
- Monitor and Improve Blood Pressure: Regularly track blood pressure and other arterial biomarkers using the Pulse to identify trends and adjust medical therapies as needed. The combination of dietary changes, stress management, and exercise with medication can improve your blood pressure and arterial health.
- Address Metabolic Health: Balance blood sugar by focusing on nutrient-dense foods, reducing sugar intake, and maintaining regular physical activity. Improve cholesterol and triglycerides by incorporating more fiber and plant sterols into your diet.
- Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol: Smoking significantly stiffens arteries, making cessation one of the most effective steps for improving vascular health. To reduce cardiovascular risks, limit alcohol to within recommended guidelines: 1 drink per day for women and up to 2 for men.
- Optimize Sleep: Sleep 7–9 hours per night to support vascular repair and regulate stress hormones.
- Personalized Testing and Care: Use the Pulse alongside other advanced tests (e.g., inflammation markers or lipid panels) to tailor a plan addressing your unique cardiovascular profile.
By focusing on these lifestyle changes, you can effectively manage your brachial blood pressure and maintain optimal cardiovascular health.
Empowering Your Heart Health Journey
By regularly monitoring and understanding your brachial blood pressure and other arterial biomarkers with the Pulse, the world’s most advanced personal arterial health monitor, you can take proactive steps towards maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system from the comfort of your home. This cutting-edge technology empowers you to make informed decisions about your health, potentially reducing your risk of serious cardiovascular conditions and enhancing your overall well-being.








