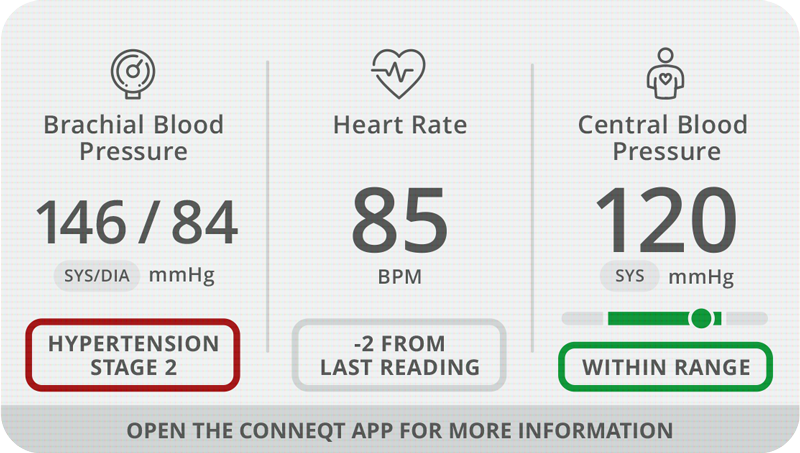
Brachial Blood Pressure - Brachial blood pressure is the pressure or force of blood on the brachial artery in the upper arm.
Why it Matters - High blood pressure can cause major cardiovascular disease if untreated or treated but poorly controlled.
Heart Rate - The number of heart beats (or contractions) per minute measured on a beat-to-beat basis.
Why it Matters - Beat-to beat heart rate is a more accurate measurement of heart rate similar to measurements obtained by an electrocardiogram.
Central Blood Pressure - Pressure exerted by the heart - a valuable health insight not provided by traditional BP cuffs.
Why it Matters - Central blood pressure reflects key vascular issues such as arterial stiffness, which makes it a more accurate predictor of subclinical cardiovascular disease than traditional brachial blood pressure alone.
Arterial Pressure Measurements
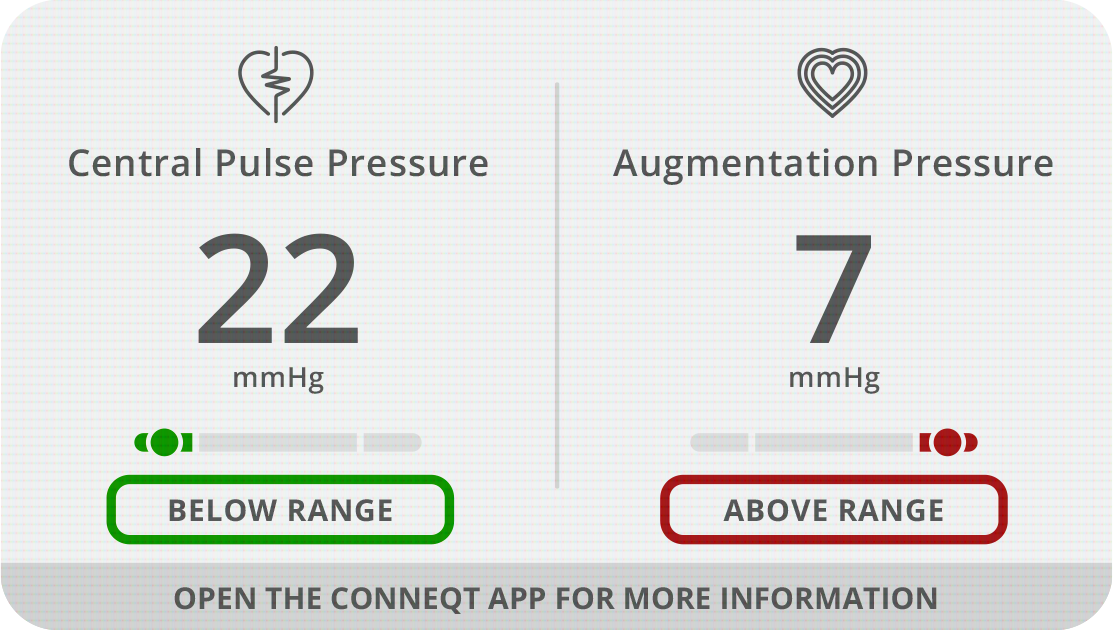
Central Pulse Pressure (CPP) - Pressure experienced by the major organs such as the brain, kidney, and liver.
Why it Matters - Central pulse pressure helps identify the risk of end organ damage to key organs like the brain, kidney and heart.
Augmentation Pressure (AP) - The increase in central aortic pressure caused by pressure wave reflection
Why it Matters - A marker of arterial stiffness, elevated augmentation pressure is associated with cardiovascular risk factors as well as increased cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
Arterial Insights
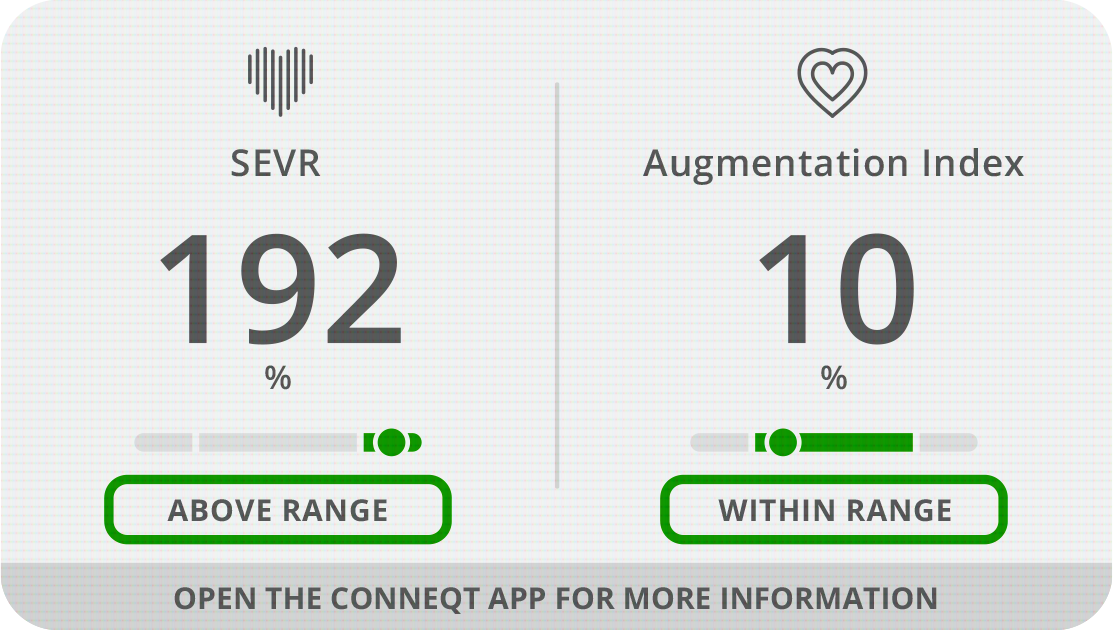
Subendocardial Viability Ratio (SEVR) - The supply & demand of oxygenated blood to the myocardium.
Why it Matters - SEVR offers insight into how well a person’s heart can handle the stress of exercise.
Augmentation Index (AIx) - A % measurement of your heart’s workload due to arterial stiffness.
Why it Matters - Chronic stress on the heart and the cardiovascular system can lead to heart failure and hypertrophy (enlarged heart).
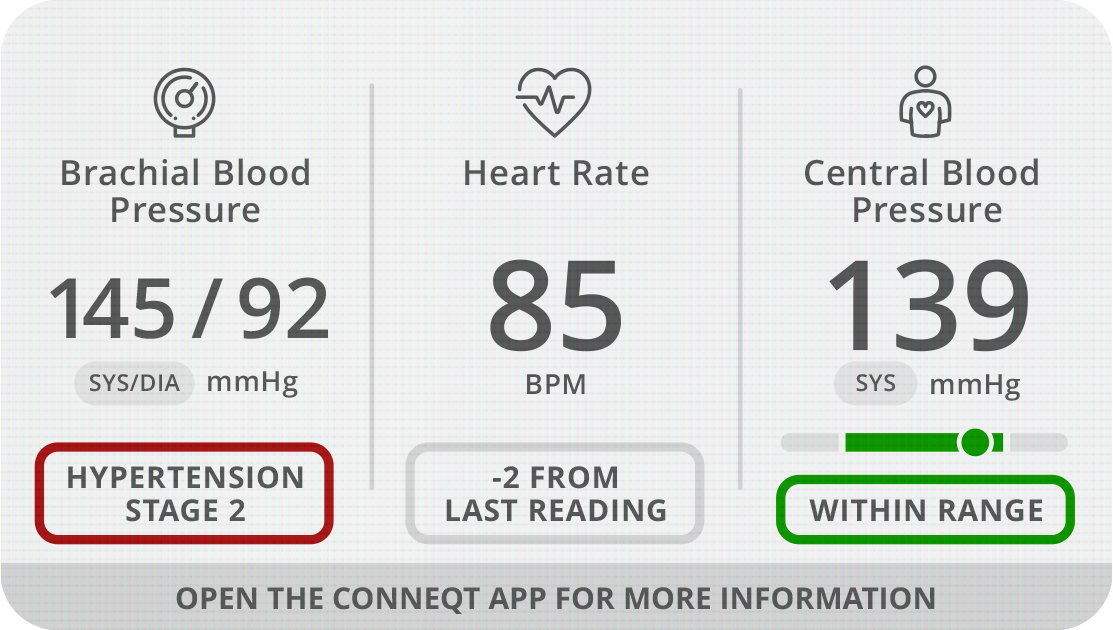
Brachial Blood Pressure
Brachial blood pressure is the pressure or force of blood on the brachial artery in the upper arm.
Why it Matters
High blood pressure can cause major cardiovascular disease if untreated or treated but poorly controlled.
Heart Rate
The number of heart beats (or contractions) per minute measured on a beat-to-beat basis.
Why it Matters
Beat-to beat heart rate is a more accurate measurement of heart rate similar to measurements obtained by an electrocardiogram.

Central Blood Pressure
Pressure exerted by the heart - a valuable health insight not provided by traditional BP cuffs.
Why it Matters
Central blood pressure reflects key vascular issues such as arterial stiffness, which makes it a more accurate predictor of subclinical cardiovascular disease than traditional brachial blood pressure alone.
Central Pulse Pressure
Pressure experienced by the major organs such as the brain, kidney, and liver.
Why it Matters
Central pulse pressure helps identify the risk of end organ damage to key organs like the brain, kidney and heart.
Augmentation Pressure
The increase in central aortic pressure caused by pressure wave reflection.
Why it Matters
A marker of arterial stiffness, elevated augmentation pressure is associated with cardiovascular risk factors as well as increased cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
Subendocardial Viability Ratio (SEVR)
The supply & demand of oxygenated blood to the myocardium.
Why it Matters
SEVR offers insight into how well a person’s heart can handle the stress of exercise.
Augmentation Index
A % measurement of your heart’s workload due to arterial stiffness.
Why it Matters
Chronic stress on the heart and the cardiovascular system can lead to heart failure and hypertrophy (enlarged heart).